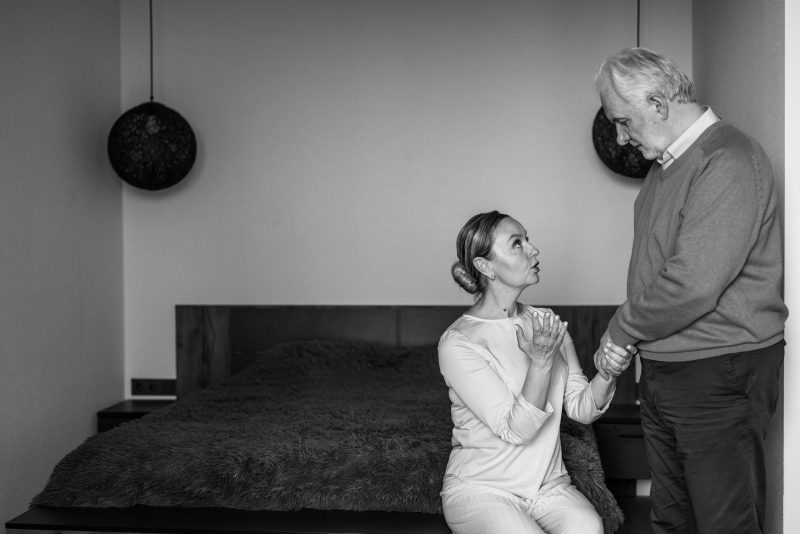
As you progress through life’s journey, one inevitable stage you encounter is aging. With it comes a myriad of physical, psychological, and social changes that impact individuals and their relationships with family members. This evolving dynamic often requires adult children to step into caregiving roles for their aging parents, while older adults increasingly rely on their children or other family members for support.
Navigating the challenges within aging families can be a delicate task, particularly when differing expectations and values regarding care and support for older adults come into play. For example, one family member may believe a certain medical procedure is necessary, while another may disagree. These differences have the potential to create conflict and tension.
To address these challenges, families must take a proactive approach. Recognizing the potential challenges of caring for aging loved ones is crucial in providing the support they require. Through collective effort and a willingness to seek external assistance when necessary, families can ensure their elderly loved ones receive the care and attention they deserve while nurturing and preserving the bonds that tie them together.
This article aims to provide valuable insight and tips to assist families in their journey of caring for elderly parents. By covering various aspects of aging, including the physical and emotional situations, living environment, financial considerations, healthcare management, and preventing loneliness, the article aims to equip you with the information and practical advice needed to navigate this meaningful chapter in your family’s life.
Understanding the concept of ‘aging’
To understand the concept of ‘aging,’ you should start by asking yourself: “What is aging, and who are the elderly?”
Aging encompasses the natural progression of processes that gradually reduce an individual’s physical or mental capabilities, increasing the likelihood of a permanent decline in these capacities over time. The elderly are individuals who have reached an advanced age, typically considered 65 years or older.
However, it is important to note that aging is a natural process affecting everyone and is a complex process beyond chronological age.
Signs that the elderly need help
Next, you need to ask yourself, “Do the elderly in my family need help?” To answer your question, you may pay attention to these physical, cognitive, and emotional indicators of aging or signs that the elderly in your family needs help.
Changes in physical abilities
Muscle weakness and joint pain are common among the elderly. However, if your parents or grandparents are having serious difficulty, you must look out for these signs as they need help (Fielding et al., 2022; Jackson et al., 2012; Kenny et al., 2008):
- Declines in physical function. Older people may experience a decreased ability to perform daily tasks or physical activities they once did easily, such as walking, climbing stairs, or carrying groceries.
- Decreased muscle strength. Older adults may notice reduced muscle strength, leading to difficulty lifting objects, getting up from a chair, or maintaining balance.
- Changes in body composition. Aging can result in an increase in fat mass and a decrease in fat-free mass (muscle and bone density). This shift can lead to changes in overall body shape and an increased risk of obesity-related health issues.
- Reduced physical work capacity. Older individuals may experience a decrease in their ability to engage in physical tasks or work due to reduced aerobic and musculoskeletal capacity. This decline can impact their endurance and stamina.
Cognitive decline
This refers to the concern or difficulty with a person’s thinking, memory, and concentration. Cognitive changes in aging that may sign the elderly need help (Harrington et al., 2018; Huang et al., 2020):
- Declines in verbal memory. Older adults may experience difficulties recalling and retaining verbal information, such as forgetting names, conversations, or recent events.
- Working memory challenges. Aging can result in reduced working memory capacity, making it harder to hold and manipulate information in the mind. This may lead to difficulties in multitasking, following complex instructions, or remembering and executing plans.
- Executive function impairments. The ability to manage and control cognitive processes, such as problem-solving, decision-making, and attentional control, may decrease with age. Older individuals may struggle with organizing tasks, switching between activities, or solving complex problems.
- Slow processing speed. Aging is associated with a gradual decline in information processing speed. Older adults may take longer to process and respond to new information, leading to delays in decision-making or difficulties keeping up with fast-paced tasks.
- Changes in perception and cognition. Aging can bring about variable declines in perception and cognition. Older individuals may notice changes in their ability to perceive sensory information accurately or experience challenges in thinking, reasoning, and understanding complex concepts.
Emotional changes
The changes brought on by aging might trigger various emotions in the elderly. Be alert to the emotional shifts in aging since that may be a sign they need help (Hsu, 2011; Waldman-Levi et al., 2020):
- Reduced engagement and well-being. Emotional well-being plays a vital role in older adults’ participation in activities and their overall satisfaction with life. If you notice a decline in their interest or motivation to engage in social interactions or hobbies they once enjoyed, it could be a sign that they need assistance.
- Impact of life events. Significant life events, such as the loss of a loved one or major life transitions, can have a profound emotional impact on older adults. If you observe persistent sadness, grief, or a decline in their overall emotional state following such events, it may indicate that they require support.
- Emotional challenges related to health conditions. Chronic health conditions can lead to emotional difficulties in older adults. Managing ongoing health issues, experiencing limitations in daily activities, or coping with the loss of independence may result in feelings of anxiety, sadness, or depression.
While the presented aging indicators can be useful in spotting signs of decline in the elderly, it’s important to remember that some of these changes might also result from other factors. For example, declines in cognitive function may be related to conditions such as depression or anxiety rather than age-related changes in the brain.
Additionally, some individuals may experience slower declines in physical function or cognitive abilities due to genetic or lifestyle factors. Therefore, it is important to note that aging is a natural process, not a disease, affecting each individual differently.
Building a healthy lifestyle for the elderly
As people age, their bodies and minds undergo changes that can make it more difficult to maintain good health. By promoting healthy habits and providing support, families can help older adults stay healthy for as long as possible. Here are the five components of the Healthy Lifestyle Index (HLI) (Atallah, 2018):
Weight management
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for overall well-being, especially as people age. Encouraging the elderly to adopt a balanced diet and engage in regular physical activity can help them manage their weight effectively.
Smoking status
Quitting smoking or avoiding tobacco use altogether is vital for promoting healthy aging. Supporting the elderly in their efforts to quit smoking can significantly improve their long-term health outcomes.
Physical activities
Staying physically active is key to maintaining strength, flexibility, and cardiovascular health. Encouraging older people to engage in regular exercise or physical activities that suit their abilities can contribute to their overall well-being.
Alcohol consumption
Monitoring alcohol consumption is important for older adults to maintain their health. Moderation is key, and it is crucial to educate and support the elderly in making informed choices regarding alcohol intake.
Healthy diet
A nutritious diet plays a crucial role in healthy aging. Encouraging the elderly to adopt a balanced and varied diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can provide them with essential nutrients and contribute to their overall health.
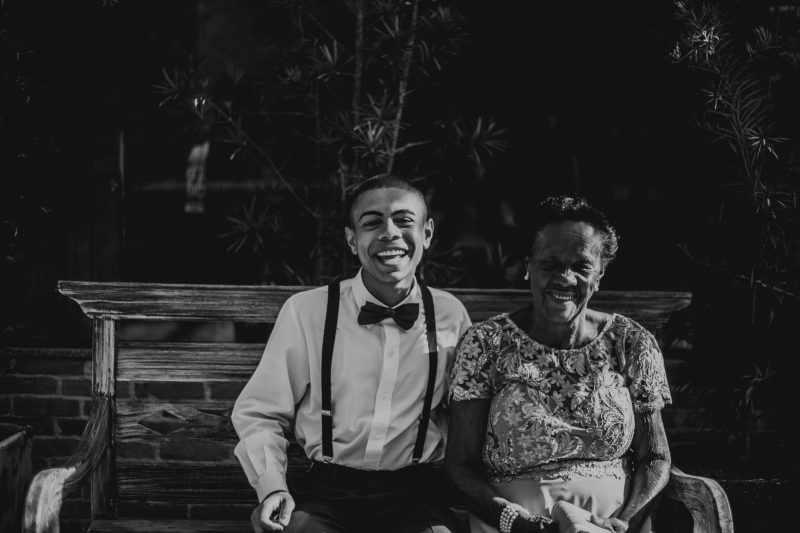

By focusing on these five components of the HLI, families can support the elderly in building and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Offering guidance, education, and assistance tailored to their needs and abilities can significantly enhance their quality of life and promote healthy aging.
5 Home safety tips for elderly family members
It is vital for the elderly to have a safe home, as it can help them maintain their independence and dignity while also reducing the risk of accidents and injuries.
It also provides peace of mind for their loved ones, knowing they live in a secure and comfortable environment. Adapted from Sheth & Cogle (2023), here are five ways you can create a safe living environment for your aging family members:
Conduct a home safety inspection
Begin by inspecting the home to identify hazards that could lead to falls or accidents. Pay attention to walkways, stairs, bathrooms, and living spaces.
Implement appropriate modifications
Based on the home safety inspection, make the necessary modifications to reduce risks. Install grab rails in essential areas like bathrooms and staircases to provide stability and support. Consider using non-slip floor surfaces or mats to prevent slipping.
Use adequate lighting
Ensure sufficient lighting throughout the home to enhance visibility and reduce the risk of falls. Well-lit areas include hallways, entrances, and staircases. Consider using motion sensor lights for added convenience and safety at night.
Seek professional assessment
Consult with an occupational therapist or other trained professional for a comprehensive evaluation. They can provide personalized recommendations for home modifications and suggest additional components, such as clinical, physical activity, or behavioral interventions.
Regular maintenance
Regularly inspect the home for any safety issues or maintenance needs. Promptly address any concerns, such as repairing loose handrails or uneven flooring, to maintain a safe living environment.
By following these steps and prioritizing home safety, you can create a secure living environment for the elderly, minimizing the risk of falls and promoting a safe home.
Managing medications and healthcare needs
As your loved ones age, their health needs become more complex and require careful attention. Proper medication management can prevent dangerous drug interactions and ensure they receive the correct dosage of their medications.
Regular healthcare check-ups can also catch any potential health issues early on, allowing for timely treatment and better outcomes. By actively managing their healthcare needs, you can help your elderly family members maintain their independence and quality of life for as long as possible.
Adapted from Albert et al. (2022) and Tett et al. (1993), here are some practical tips for caregivers to manage the medications and healthcare needs of elderly family members:
Engage with pharmacists
Seek assistance from pharmacists who specialize in geriatric care. They can provide valuable interventions such as verbal counseling, written medication information, memory devices, and audiovisual techniques to support medication management. Remember that the effectiveness of these interventions may vary.
Active caregiver involvement
As a caregiver, actively participating in medication management for your elderly family members is important. Assist with tasks like ordering medications and maintaining medication schedules. Your involvement is crucial in ensuring they receive the right medications at the right times.
Regular medication counseling
Schedule regular counseling sessions with healthcare professionals to discuss medication-related concerns. These sessions provide an opportunity to address questions, identify potential side effects, and optimize medication management strategies based on changing healthcare needs.
By following these tips, you can effectively manage medications and address the healthcare needs of your elderly family members as a caregiver. Your active involvement, collaboration with healthcare professionals, and continuous evaluation will improve their overall well-being and medication safety.
Financial considerations for caregivers
As people age, their healthcare needs may increase and become more expensive. It’s important to plan and consider the financial resources needed to provide them with the required care.
This can help alleviate stress and ensure they receive the best possible care while also preserving their financial stability. Adapted from Xu et al. (2006), here are some tips for caregivers to consider the healthcare costs and resources for elderly family members:
Be mindful of healthcare costs
Healthcare expenses can be a significant burden for elderly individuals and their families. As a caregiver, carefully consider the financial aspects of healthcare.
Be aware that their financial situation can affect their access to healthcare services and the choices available to them. Explore options for financial assistance, discounts, or programs designed to alleviate the cost of medications, treatments, and healthcare services.
Ensure adequate insurance coverage
Explore different insurance options and strive to secure appropriate coverage for your elderly family members. Insurance increases the likelihood of healthcare service utilization, ensuring they can receive necessary medical care.
Seek support and resources
Stay informed about available healthcare resources, support groups, and organizations that assist caregivers and elderly individuals. These resources can offer valuable guidance on navigating healthcare costs, accessing affordable medications, and exploring financial aid options.
By considering healthcare costs and resources for your elderly family members, you can help ensure they receive the necessary medical care without undue financial strain. Be proactive in exploring insurance options, seeking support, and advocating for their healthcare needs to enhance their access to quality healthcare services.
Preventing loneliness among the elderly
Loneliness can negatively affect the physical and mental health of the elderly. By actively working to prevent loneliness among elderly family members, you can help them maintain a higher quality of life and overall well-being. Here are some tips for caregivers to help their elderly family members prevent loneliness:
Encourage social engagement
Support your elderly family members to participate in social activities that align with their interests and abilities. This could include joining community groups, clubs, or organizations where they can interact with like-minded individuals and form new friendships.
Promote physical activity
Physical activity contributes to overall well-being and provides opportunities for social interaction. Encourage your elderly family member to join in walking groups, exercise classes, or outdoor hobbies involving socializing with others.
Support intergenerational interactions
Foster opportunities for intergenerational interactions where older adults can engage with younger individuals. This can include volunteering at schools, participating in mentorship programs, or joining intergenerational community initiatives.
Provide access to technology
Ensure that your elderly family member can access technology, such as smartphones or tablets, to facilitate communication and connection with others.
Implementingthese strategies can help prevent loneliness among elderly family members and promote their overall well-being. Remember, fostering social connectedness, supporting engagement, and providing opportunities for meaningful interactions are key to enhancing their quality of life.
In conclusion
On the journey through life’s later chapters, caring for elderly family members requires a proactive and compassionate approach. Navigating the challenges that arise within aging families can be complex.
However, by recognizing the signs of aging, building a healthy lifestyle, creating a safe home environment, managing medications and healthcare needs, considering financial resources, and preventing loneliness, families can provide the support and care their elderly loved ones deserve.
Through collective effort, understanding, and the willingness to adapt, families can embrace this meaningful chapter and nurture the bonds that tie them together, ensuring that their elderly family members experience a fulfilling and dignified journey through aging.
If you would like to see more resources on aging, visit the Family Science Labs. The lab uses the research of the Institute for Life Management Science to produce courses, certifications, podcasts, videos, and other tools. Check out the Family Science Labs today.
Photo by Edward Eyer and Pavel Danilyuk on Pexels