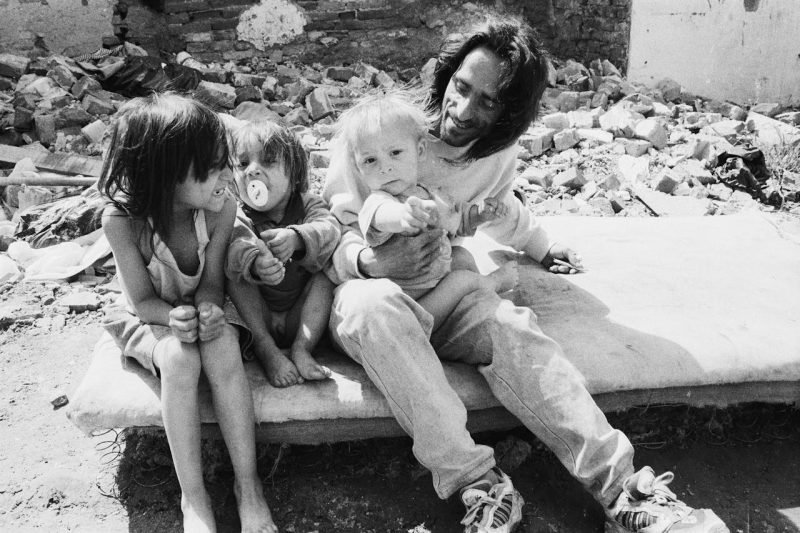
Poverty is not only an economic issue; globally, it affects living conditions and shapes home environments. In the contemporary world, the majority experience difficulty surviving within the walls of their homes and struggle to maintain a home environment conducive to healthy living.
The detrimental effects of poverty reach far and affect your physical and mental well-being. It affects the overall quality of life, amplifies familial conflicts, and disrupts home environments.
To minimize the negative effects of poverty on home environments, the article seeks to uncover the layers of this complex issue, provide insights into the consequences of being poor, and encourage action-oriented strategies to facilitate survival. Read more to find out how to improve home environments and to creating nurturing and safe home spaces despite poverty.
Unraveling the impact of poverty on home environments
Uncertain economy and inflation have affected millions of lives, specifically families living in low-income communities.
According to the global poverty trends, 26% (1.85 billion people) and 46% (3.71 billion people) lived below the threshold of $3.65 and $6.85 per day, respectively, in 2022. Additionally, around 8.5% (682 million people) lived in extreme poverty.
Every day the majority of American households with a family of four survive on $27,000 per year while a single person lives on $15,000 every year. In 2022, approximately 62% of people living in Sub-Saharan Africa experienced extreme poverty. In 2021 and 2022, more than 22% (14.4 million people) of UK residents lived in poverty including 8.1 million working-age adults, 4.2 million children, and 2.1 million pensioners.
Scarcity of resources
In 2021, one in eight American households (around 12.5%) could not afford sufficient food for their families, compared to households without children (9.4%), Latin (16.25%), and Black (19.8%) households.
Families and children affected by poverty often lack educational opportunities and resources (e.g., supplies, books, and appropriate technology) and attend overcrowded and under-resourced schools. Therefore, poverty is associated with homelessness, substandard housing, unsafe neighborhoods, hunger, inadequate childcare, and under-resourced schools.
Housing challenges amidst poverty
Accessing a tenancy is becoming increasingly difficult due to the lack of affordable housing. Extreme market competition results in vulnerable and low-income households paying unaffordable rents, moving to cheaper locations, and living in poor-quality properties.
Globally, housing crises were observed in the last half of 2020 and the first half of 2021. For instance, housing prices rose by 11% in America, whereas they rose by 22% in New Zealand during the period. Also, Hong Kong maintained the title of unaffordable housing market in 2020, as the average housing price is 20.8 times higher than household income.
Additionally, tension arises with using space in multigenerational families or overcrowded households. Household type may positively or negatively influence the renting experiences of low-income families. Some may choose to live alone, which can be a high financial burden amidst high housing costs, while many prefer to share for economic reasons.
Impact on children and familial relationships
Low-income households with children are at increased risk of financial poverty. For instance, they are vulnerable to transport-related challenges. Being mobile is crucial to one’s social life; however, financial investment in transportation like bicycles, cars, and public transport tickets is challenging for low-income families.
Additionally, low-income children have a high risk of emotional, cognitive, and health-related problems, such as:
- Inadequate nutrition
- Asthma
- Pneumonia
- Low birth weight
- Developmental delays
- Poor emotional and social functioning
- Adverse effects on executive functioning
- Poor academic achievements
- Behavioral problems.
Furthermore, economic stress strains familial relationships as it intensifies insecurities and tensions, resulting in poor communication and conflicts. As families struggle with limited resources, disagreements about spending habits, budgeting decisions, and financial priorities often escalate to conflicts that strain relationships.
The economic stress contributes to frustration, depression, and anxiety. Ultimately, it hinders developing and maintaining a positive home environment.
Alleviating the toll of poverty on households
Implementing actionable strategies is important to address and alleviate the impact of poverty on society and households, which may lead to sustainable improvement in their living conditions and overall well-being.
Community support and resources
Community support acts as a barrier that helps households affected by poverty build resilience and resolve emerging stressors in their daily life.
Read more: Embracing Community Living: Building a Healthy Environment in Residential Living
Collaboration between residents allows the effective accumulation of local resources through clothing drives and food banks that ensure equal distribution of necessities to households.
Local programs can be established through community support, such as educational programs, mentorship, skill-developing workshops, and vocational training to enhance learning and employability. Also, supporting small businesses within the community offers opportunities to reduce the impact of poverty.
Read more: Weaving Unity: Essential Tips for Cultivating Community Belongingness
If you are seeking assistance, reach out to local community organizations or groups to share your concerns and utilize the resources they provide. Take the first step and choose to ask for support — it showcases your strength and willingness to overcome challenges.
Educational opportunities
Equitable accessibility to education and skills development has become crucial in a rapidly changing economy, which catalyzes change among poverty-experienced households. Education provides employment opportunities, develops skills, and fosters critical thinking, resulting in an escape from systemic poverty.
To improve educational resources in impoverished areas:
- Investments in infrastructure and well-equipped schools that are conducive to learning need to be constructed.
- Training programs need to be implemented along with attractive incentives to access quality education through skilled educators.
- Contributions towards the accessibility of technology should be made to offer e-learning in poverty-driven areas.
- Financial aid programs and scholarships should be available to attenuate the economic stress of families with children pursuing education.
Seize the opportunity by utilizing available educational resources. Your actions today will create employment opportunities and break down barriers to systemic poverty.
Advocacy and policy change
Advocating for policy changes and creating policies can help address the systemic issues induced by poverty within society. For instance, creating policies to reduce income inequality, including the application of progressive taxation and an increase in minimum wage, can help improve the financial well-being of low-income households.
Policymakers can support disrupting the cycle of intergenerational poverty by investing in high-quality education from early childhood through vocational training. Moreover, guaranteeing affordable healthcare services can prevent households from experiencing poverty due to high medical costs.
Although systemic adjustments are crucial, it is important to design policies based on the lived experiences of individuals and families. Collaborating with individuals and communities provides in-depth insight into their challenges and strategies for overcoming them.
The participatory and inclusive approach aids in creating effective policies and fosters empowerment among affected households.
You can engage in advocacy by:
- Staying informed about national and local policies by participating in community-based conferences and discussions.
- Volunteering with organizations and voicing concerns to local and national elected officials for systemic change, particularly for affected households.
- Engaging with social media platforms to raise awareness and collectively call up for policy changes that prioritize equality and implement strategies to mitigate poverty.
In conclusion
Every household desires to create a life that fulfills its necessities, including housing, nutrition, health, and education. However, poverty enters the picture and adversely impacts living conditions, familial relationships, well-being, and quality of life.
The interconnected issues of housing challenges and scarcity of resources (e.g., the unaffordability of sufficient food, books, etc.), and their profound outcomes indicate the urgency of addressing systemic poverty.
To mitigate poverty and promote healthy living, you need to build community support, ensure equitable accessibility to quality education, and advocate for policy adjustments. So, take action today by raising your voice for policy adjustments to improve living conditions.
If you would like to see more resources on home environment, check out the Personal Science Labs. The lab uses the research of the Institute for Life Management Science to produce courses, certifications, podcasts, videos, and other tools. Visit the Personal Science Labs today.
Photo by István Süli on Pexels