Whether you’re a student, project manager, or business owner, managing complex projects often feels tricky and difficult. Your ideas can scatter, priorities remain unclear, and important details slip through the cracks, resulting in a loss of time and productivity. If you’ve ever felt overwhelmed trying to keep everything aligned, you’re not alone.
But don’t worry, there’s a simple fix: mind mapping. Effective mind mapping practices give you a visual way to organize chaos and improve your workflow’s concentration, creativity, and productivity.
While many people are familiar with its general definition, the exact practice is relatively unknown in productivity spheres. This article discusses mind mapping techniques and how they can transform your idea organization. It’s time to explore the benefits of using mind maps to simplify complexity and take charge of your projects now. Read on to find out how.
What is mind mapping and how it works
Tony Buzan popularized mind maps in the 1970s. They are now widely used by students, professionals, and creatives as a visual method of organizing information.
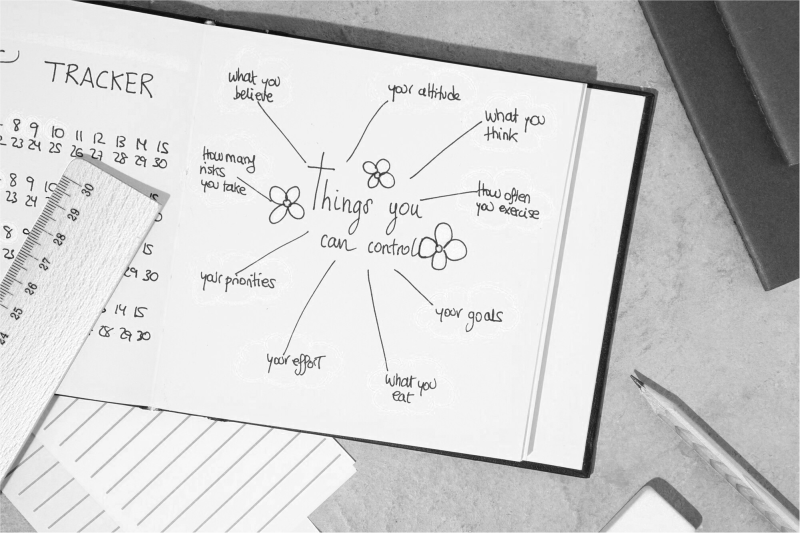
Mind mapping is a diagram representing tasks, words, concepts, or items linked to and arranged around a central idea or subject using a non-linear graphical layout that allows the user to build an intuitive framework around a central idea.
The structure mimics how your brain naturally processes and organizes information. Each branch and sub-branch builds an intuitive hierarchy that helps users manage tasks, capture insights, and connect ideas.
Here’s a breakdown of the key elements that make up an effective mind map:
Central node (core idea or topic)
Every mind map begins at the center, with a central node — the anchor that holds the entire structure together.
This is typically your main subject or goal, such as “Product Launch,” “Climate Change,” or “Final Exam Preparation.” Positioned right in the middle of the canvas, it represents the core theme from which all other ideas branch outward.
The central node is often made visually distinctive to ensure it stands out, using a larger font, bold text, or a bright, unique color. Its placement and design signal its importance, drawing the viewer’s eye immediately to the starting point of your thought process.
Main branches (primary categories or themes)
Radiating from the central node are the main branches.
These represent the major components or key categories directly related to your core idea. For example, if your central theme is “Marketing Plan,” the main branches might be labeled “Content Strategy,” “Target Audience,” “Budget,” and “Timeline.”
Each branch typically uses concise, keyword-rich labels that are easy to scan and grasp quickly. Many mind map users color-code these branches for visual clarity and thematic separation.
This organizes information logically and boosts recall by tapping into visual learning pathways.
Sub-nodes (supporting details or subtopics)
Attached to each main branch are smaller offshoots known as sub-nodes, which explore the specifics of each category more deeply.
These sub-nodes break down broader ideas into more detailed components — for example, under the “Budget” branch, sub-nodes might include “Ad Spend,” “Tool Subscriptions,” or “ROI Goals.”
Sub-nodes use short phrases or bullet points instead of complete sentences to make the content easier to remember. This layered structure lets you drill down into a subject without losing sight of the big picture — a hallmark benefit of using mind maps to manage complex ideas.
Keywords
Keywords are the lifeblood of an effective mind map.
Instead of long-winded explanations, concise and meaningful words or phrases represent ideas. This simplicity promotes quick understanding and mental association, allowing users to absorb and recall information faster.
For example, rather than writing “Develop a full marketing strategy for Q3,” a well-designed map might simply use “Q3 Strategy” or “Q3 Marketing.” This lean approach reduces clutter and keeps the visual layout clean and impactful.
Colors
Colors are a strategic tool in concept mapping.
You can assign each branch or sub-topic a specific color to represent a theme, priority level, or category. This makes it easier to track ideas visually.
For example, red might be used for urgent tasks, green for creative ideas, and blue for research-based content. Over time, your brain learns to associate these colors with specific functions.
Visual elements (icons, images, diagrams)
Many mind mappers include visual cues, such as icons, images, and diagrams, to further enhance clarity and engagement.
Icons can indicate task status, such as a checkmark for completed items or a flag for high-priority tasks. Images like a lightbulb for brainstorming or a calendar for scheduling can quickly convey meaning.
Some mind maps also include arrows or connecting lines between different nodes to show relationships or dependencies across topics, reinforcing how ideas link together.
How mind mapping simplifies complex projects
Mind mapping techniques enable you to comprehend the overall picture without losing sight of the little details.
This approach not only helps you arrange your ideas, but it also highlights opportunities, goals, and patterns that you would otherwise overlook. It is a helpful tool that blends logic and creativity, making it perfect for anybody trying to increase project efficiency without compromising originality.
Here’s how this straightforward method produces significant outcomes.
Breaks down large ideas into manageable parts
Whether you’re prepping a presentation, mapping out a thesis, or starting a new project, this first step is always the hardest. The idea feels too massive. Too abstract.
That’s where mind mapping will help. Instead of letting that idea swirl around your brain, you put it down.
Central node first. Then you start breaking it apart—categories, themes, to-dos, milestones. Each branch simplifies the chaos. Each subtopic feels doable. And when everything’s laid out visually, you stop spinning your wheels and start gaining traction.
In educational settings, mind mapping aids students in organizing and prioritizing information, enabling them to tackle complex problems systematically. Students use mind maps not just to take notes, but to make sense of them. They learn to sort, connect, and prioritize. Complex theories turn into clear structures. Abstract concepts become tangible.
Enhances clarity and focus
Information overload is real. And when your brain is juggling five tabs of thought at once, it’s easy to lose sight of the bigger picture.
But mind maps force structure, not in a rigid way, but in a way your brain loves. The most important stuff goes right at the center. Everything else branches out, one layer at a time.
A study shows that mind mapping can boost retention by 10-15% when studying and revising. Students who worked on mind maps individually reported being more focused, with more time to read, connect ideas, and reflect, leading to deeper engagement and better retention.
Another study shows that students appreciated how mind maps allowed them to see how the information was connected, making it easier to understand relationships between concepts and ideas.
Read more: How to Focus and Get Things Done
Encourages creative problem solving
Sometimes, solving problems isn’t about working harder. It’s about seeing things differently.
Mind mapping unlocks that shift. It pulls you out of linear thinking and throws your ideas into open space. Suddenly, a stuck idea has room to move, and a problem has multiple paths forward.In teaching settings, using mind maps allows students to become more actively involved in their learning process, which can then inspire more interest in what is being learned.
Unlike traditional linear lists, mind maps allow thoughts to flow in all directions, mimicking how your brain naturally works. This nonlinear approach supports creative thinking, encouraging new associations, fresh perspectives, and out-of-the-box solutions.
Actionable insights for using mind mapping techniques
To truly benefit from mind mapping, it’s not enough to understand the concept — you need practical, proven ways to apply it. So, if you’re wondering “how do you create a mind map?”, here’s a practical guide you can follow:
Doing mind mapping effectively
Creating a mind map is a simple yet powerful way to organize ideas and simplify complex tasks. Here’s how to do it effectively:
- Place your main topic or goal. This could be a project name or core concept in the center of your page or screen. This central node will act as the anchor for all related ideas and themes.
- Identify key categories, themes, or components. These relate to your central idea. Create branches that radiate outward from the center to represent each of these subtopics.
- Add sub-branches. For each subtopic, add sub-branches that further break down the idea into smaller, manageable parts. These can include tasks, examples, questions, or related ideas.
- Continue branching as needed. There’s no limit to how deep you can go.
- Add relationships. Draw lines between related ideas across different branches to highlight cross-connections.
- Add other indicators. Apply colors, icons, or symbols to differentiate topics, indicate priorities, or emphasize important relationships. Use sticky notes, images, or sketches to make your map more engaging and memorable.
- Add more info. Enrich each branch with supporting information: links, notes, research data, or references.
Revisit your mind map regularly to refine connections, reorganize thoughts, or add new information. Keep it dynamic and change as your project changes.
Tools and platforms for digital mind mapping
While pen-and-paper mind mapping is simple and satisfying, it has limitations, like a lack of editing flexibility, limited space, and no backup. Digital mind mapping tools solve these problems and add powerful planning, sharing, and collaborating features. Here are some top options to consider:
- Web-based mind map creators. Ideal for real-time collaboration, these tools offer intuitive interfaces with drag-and-drop functionality, ready-made templates, and the ability to share maps instantly with others. Many support cloud storage and integrations with productivity platforms.
- Advanced layout and design platforms. These tools support a variety of visual formats such as tree charts, timelines, fishbone diagrams, or flow-based layouts. They often have elegant themes and offer flexible export options like PDF, PNG, or text formats.
- Visual whiteboard collaborators. Designed for remote teamwork, these platforms blend mind mapping with brainstorming and project planning tools. They provide virtual whiteboards where teams can work together in real time.
- Diagram-focused mapping tools. These combine mind mapping with flowcharts, concept mapping, and other structured diagramming features. They’re ideal for creating process maps, organizational charts, system diagrams, or visualizing interrelated structures within a project or strategy.
- Simple, lightweight mind map makers. Perfect for quick idea capturing, note-taking, or planning small tasks. These tools emphasize ease of use with clean layouts, colorful branches, and features like unlimited image uploads, link attachments, and version tracking.
Read more: Need Help in Time Management? There’s an AI Tool For That
Real-world examples and applications
Mind mapping techniques are highly adaptable and can bring structure and clarity to various professional and personal contexts.
Mind mapping can transform that chaos into clarity if you’re a student staring down a mountain of revision notes during finals week.
Instead of juggling scattered ideas from multiple subjects, a digital mind map lets you visualize everything in one place. Start with your subjects — say, psychology, literature, and statistics — and break them down into chapters, then key terms, and even formulas.
The same approach applies in team settings. A mind map can align your team across time zones and specialties if you’re managing a collaborative project, like a website redesign.
Begin with the central project goal, then branch into areas like design, development, content, and testing. Under each branch, assign owners and deadlines.
This visual format helps everyone share an understanding of the big picture and the fine details, eliminating confusion and making the project feel achievable.
In conclusion
Complex projects can easily leave you feeling overwhelmed, scattered, and unsure where to begin. But it doesn’t have to be that way. Instead, use mind mapping.
Mind mapping is a shift in how you think. It helps you take the clutter in your head and turn it into something structured, clear, and actionable. What once felt overwhelming suddenly becomes manageable. And the more you use it, the more natural it becomes.
And it’s not just for you. Mind maps make your ideas easier for others to understand, too, whether explaining a plan to your team or pitching a strategy to stakeholders.
So if your ideas feel scattered or you’re unsure where to begin, try mapping them out. You might be surprised at how quickly things start to make sense.
If you would like to see more resources on mind mapping, check out the Personal Productivity Science Labs today. The lab uses the research of the Institute for Life Management Science to produce courses, certifications, podcasts, videos, and other tools. Visit the Personal Productivity Science Labs today.
Photo by Freepik