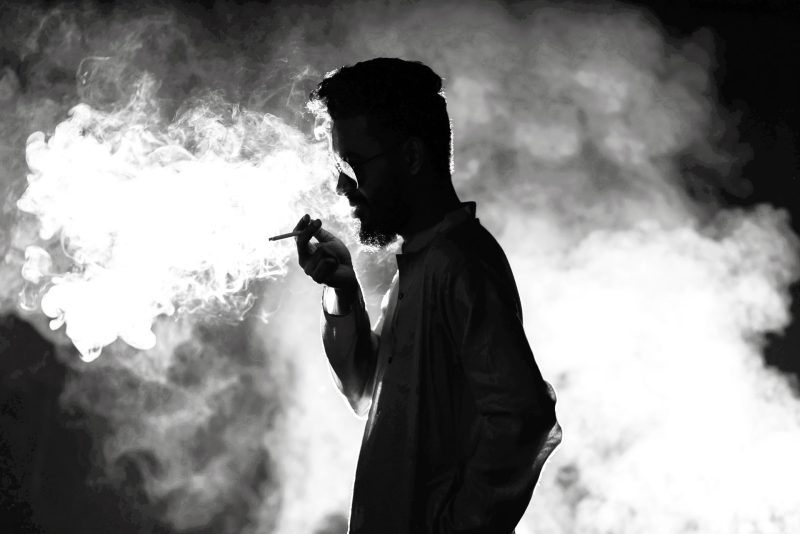
A global overview by the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) reported that a significant proportion of the global population aged between 15 and 64, males, had reportedly used drugs at least once, with an estimated number of 284 million individuals during the year 2020.
Moreover, non-substance addictions related to technology, which have rewarding behavior can also affect a high number of individuals, especially young people. The study of global prevalence research indicates a significant number of individuals experiencing addiction to smartphones (26.99%), social media (14.22%), the internet (14.22%), and gaming (6.04%) up to 2021.
Although addiction can help someone feel better or perform better in school or at work, addictive behavior has negative consequences for the individual. Addiction affects physical health, leading to conditions such as lung or heart disease, stroke, or cancer. It can also impact mental health, with conditions such as anxiety, depression, or schizophrenia potentially arising before addiction worsens.
The process and effects of addiction have garnered a lot of attention for research, from neuroscience to emotional and behavioral aspects. This article will help you understand the science of addiction and help reduce stigma and increase awareness about the challenges of addiction and recovery.
What is the clinical definition of addiction?
The American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) defines addiction as a treatable, chronic medical disease involving complex interactions among brain circuits, genetics, the environment, and an individual’s life experiences. It can be caused by an individual’s genetics and surroundings and is commonly viewed as a brain disorder. It should also be emphasized that addiction concerns the underlying neurological processes of the brain rather than observable actions.
Further, addiction is a complex condition that affects the brain’s reward system, motivation, and memory through the compulsive use of a rewarding substance or activity despite experiencing adverse consequences. These terms are not only for substance/drug dependence but also refer to behavioral disorders, such as sexual, internet, and gambling addiction.
How many types of addiction are there?
Addiction is a multifaceted disease. People can develop an addiction to anything that stimulates the reward chemicals in the brain. Even though there are many types of addiction, the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders Fifth Edition (DSM-5) classifies addiction into two primary categories: substance use disorder and behavioral addiction.
Substance use disorder
Substance use disorder heavily involves the brain’s reward and reinforcement system, which can make people experience taking drugs in a profound way. The activation of the reward system produces feelings of pleasure or euphoria and is different from dependence. Excessive substance use can cause problems and lead to neglect of everyday activities.
While there are variations in the symptoms of each type of addiction, they also share some common symptoms. This type recognizes substance-related disorders resulting from the use of 10 separate classes of drugs: alcohol, caffeine, cannabis, hallucinogens, inhalants, opioids, sedatives, hypnotics, or anxiolytics, stimulants (including amphetamine, cocaine, etc), and tobacco.
Behavioral addiction
Individuals with addictive tendencies towards specific behaviors become dependent on the pleasurable feelings resulting from those activities and compulsively act on them, to the extent that they experience withdrawal when unable to engage in them. The growing use of technology and social media has raised concerns about the potential for behavioral addiction.
DSM-5 divides two types of behavioral addiction into gambling addiction and internet gaming disorder.
The DSM-5 recognizes gambling disorder as the first non-substance addiction to be classified as a mental condition.
It is important to note that DSM-5 text states also clearly that gaming offline or on devices that do not connect to the internet can also constitute the condition of internet gaming disorder.
On the other hand, behavioral addiction is not limited to those two types alone. Although not officially recognized by the DSM-5, much research has discovered social media, shopping, sex, food, exercise, and other behavioral addiction.
What are the signs?
Even though substance use disorder and behavioral addiction work similarly in the brain system, behavioral addictions are different in that they do not produce the same physical symptoms as drug addiction.
Physical signs
Changes in physical appearance are a common effect of substance use, such as blood pressure, heart rate, weight changes, dental issues, skin changes, bloodshot eyes, constricted pupils, changes in appetite, unusual smells on breath or body, impaired coordination, and sleep problems.
Behavioral signs
A person’s behavior and habits can also change with addiction, such as:
- being unable to stop engaging in the behavior (even when wanting to cut down)
- arranging to engage in the behavior, becoming increasingly dependent
- experiencing relationship problems
- neglecting responsibilities and activities of daily living
- being unable to complete tasks
- using in risky settings
- continuing to use despite known problems
- experiencing sudden changes in behavior
- losing energy or motivation
Risk factors for addiction
The presence of signs of addiction may have contributed to the risk factors. Identifying these risk factors can help not only understand why an addiction may have developed but also to prevent the onset of addiction in the first place. This must be addressed ahead of time to prevent and manage the disease.
Addiction can be influenced by various factors, including biological, psychological, and environmental factors.
Biological factors
Biological factors such as genetics, brain chemistry, and gender can play a significant role in the development of addiction. Genetic predisposition increases the likelihood of addiction, especially when both parents have a history of substance abuse.
Changes in the levels of certain chemicals in the brain, such as dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine, can also play a role in addiction.
Also, males have a higher risk of developing substance use disorder, gambling disorder, and internet gaming disorder than females.
Psychological factors
Psychologically, personality traits such as impulsivity and pleasure-seeking behavior are associated with substance and behavioral disorders. A neurotic personality structure is also commonly found in individuals with addictive behaviors. Childhood trauma, abuse, and neglect can increase the risk of dependence in young adulthood, while mental health problems such as depression and anxiety may arise from excessive gaming.
Environmental factors
Environmental factors can also contribute to the development of addiction. Family life during childhood can play a significant role in reducing the risk of addiction, while peer groups who engage in substance or behavioral addiction can increase the risk later in life. Economic disadvantage during childhood and adolescence can also increase the risk of substance and gambling disorders.
In conclusion
Addiction is a significant issue that impacts not only individuals but also their families, friends, and society. It results from the rewarding impact of substance or behavioral activities that can modify brain chemistry, creating an involuntary desire to persist with the behavior. Despite adverse outcomes and efforts to quit, the urge to continue the behavior persists, making it difficult but not impossible to change the behavior.
To prevent and treat addiction, understanding its types, signs, and risk factors is crucial. It helps individuals understand that addiction is not merely a matter of willpower or moral failing, but rather a complex condition with multifaceted causes.
Different types of therapy and lifestyle modifications are available for treatment that is tailored to individual differences. Individuals can decrease their chances of developing addiction and seek assistance if required by recognizing the risk factors and warning signs associated with addiction.
Overcoming addiction and living a satisfying life is achievable with the proper treatment, support, and unwavering determination. Addiction recovery can also be supported by effective coping strategies such as seeking help from others, engaging in healthy activities, and using positive self-talk. Recovery from addiction requires many attempts and efforts, but there are many pathways to conquer it. As life becomes more worth living, addiction loses its domination.
If you would like to access more tools on the subject of addiction, check out the Personal Resilience Science Labs. The lab uses the research of the Institute for Life Management Science to produce courses, certifications, podcasts, videos, and other resources. Visit the Personal Resilience Science Labs today.
Photo by Azraq Al Rezoan on Pexels