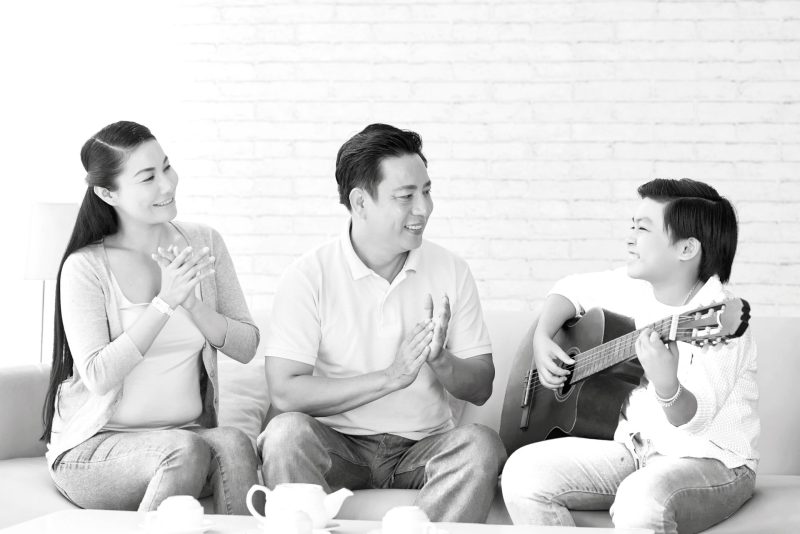
Adolescence, occurring between the ages of 10 and 19, is a challenging phase in a child’s development. During this period, children are susceptible to external influences that can significantly shape their emerging sense of identity.
Parents play a pivotal role in ensuring their children adopt positive influences, contributing to the development of a positive identity. This article explores the significance of parental influence in adolescent identity development.
Parental influence on adolescent identity development
Adolescent identity development encompasses two vital facets: self-identity and social identity, intricately intertwined throughout the journey of self-discovery and integration into society. Self-identity involves personal beliefs, values, interests, and parental influences significantly contributing to an adolescent’s self-concept.
Conversely, social identity pertains to how young individuals perceive themselves in relation to social groups, with parents playing a role in shaping affiliations and cultural connections.
Thus, parental influences are pivotal in shaping both self-identity and social identity, ultimately guiding adolescents in their quest to forge a unique sense of self while navigating the complexities of their social environment.
Parents frequently serve as primary role models during children’s development, particularly when a strong parent-child bond exists. Children naturally look up to their parents, finding in them figures to admire and emulate.
Beyond admiration, parents’ influence goes deep as children grow. This influence often transforms into a wellspring of inspiration, with some aspiring to follow in their parent’s footsteps, not only in terms of careers but also in embracing the values and principles passed down, thus perpetuating a legacy that spans generations.
Parenting styles and identity
Diverse parenting styles exist as parents bring their unique backgrounds, beliefs, and values into their approach to child-rearing. Consequently, these distinct parenting styles can have substantial effects on their children. Three prominent parenting styles are typically identified, each characterized by its own set of practices and philosophies.
Authoritarian parenting
Authoritarian parents often bypass involving their children in problem-solving, favoring rule-setting and punishment over teaching better decision-making. This strict approach can lead to obedient children but may hinder their independent thinking, decision-making abilities, and problem-solving skills, impacting their overall development and self-esteem.
Children raised by authoritarian parents may display hostility or aggression, often dwelling on anger towards their parents or themselves for not meeting expectations and, in some cases, resorting to dishonesty as a way to avoid punishment.
Authoritative parenting
Authoritative parents proactively work to prevent behavior issues from arising, employing positive discipline methods such as praise and reward systems to encourage positive behavior.
Children brought up with authoritative parenting typically experience happiness and success, and they often develop strong decision-making skills and the ability to assess safety risks independently.
Permissive parenting
Permissive parents are typically lenient, stepping in only for serious issues and often adopting a “kids will be kids” attitude. They may not consistently enforce consequences and sometimes revoke them if a child pleads or promises to behave. Taking on more of a friend than a parent role, they encourage open communication but tend to be lax in discouraging poor choices.
Consequently, their children may exhibit more behavioral problems, display a lack of respect for rules and authority, and experience lower self-esteem and increased sadness.
Positive parental support for self-discovery
When parents recognize the significance of their support in shaping their children’s adolescent identities, it can lead to more favorable and fulfilling outcomes, benefiting both the parents and their children.
Co-regulation
A valuable approach to enhance your child’s identity development is practicing co-regulation. This method involves your consistent presence as a parent, nurturing emotional growth, and teaching your child how to manage their feelings in various situations, fostering resilience and emotional intelligence, both crucial for healthy identity formation.
Co-regulation also promotes open communication between parents and children, strengthening the parent-child bond and facilitating meaningful discussions about identity, values, and personal growth, contributing to overall development.
Read more: Growing Together: The Importance of Parent-Child Co-Regulation
Open communication
There are also several other things that parents can do in order to foster adolescent self-discovery. For example, engaging in open and constructive conversations about career paths, personal interests, and life ambitions enables adolescents to gain a deeper understanding of themselves and their aspirations.
By doing so, parents can guide their children towards a path that aligns with their values and passions, setting the stage for a more fulfilling and purpose-driven life.
Equally vital is positive communication, creating an open, supportive dialogue environment that makes adolescents feel valued and heard, enhancing their self-esteem and self-worth for a strong sense of self.
Encouraging self-reflection
Teaching self-reflection is crucial as it encourages adolescents to contemplate their thoughts and feelings, fostering a deeper self-connection and promoting self-awareness, strengths, weaknesses, and values. This journey equips them with resilience and self-assurance to tackle life’s challenges.
Promoting inclusivity and diversity
Fostering diversity and inclusivity plays a pivotal role in nurturing self-discovery. Exposure to diverse cultures, perspectives, and experiences expands horizons, fostering appreciation for uniqueness and nurturing understanding and respect for others’ differences.
These efforts collectively empower adolescents to embrace their individuality and embark on a path of personal growth and self-realization.
In conclusion
Parents’ influence in forming children’s identities is undeniably significant. It is incumbent upon parents to recognize this influence and consciously integrate effective guidance and positive reinforcement into their parenting styles. Doing so creates a supportive environment that empowers children to explore and construct their identities with confidence and security.
This approach not only fosters healthy self-esteem and resilience but also encourages open communication, enabling parents to engage in constructive discussions about values, aspirations, and personal growth.
Ultimately, acknowledging their vital role in identity development allows parents to guide their children on a path of self-discovery that enriches their overall well-being.
If you would like to see more resources on adolescence autonomy and identity, check out the Parenting Science Labs. The lab uses the research of the Institute for Life Management Science to produce courses, certifications, podcasts, videos, and other tools. Visit the Parenting Science Labs today.
Photo by pressfoto on Freepik