In 2018, the total amount of municipal solid waste (MSW) generated in the US was 292.4 million tons, and 146.1 million tons of those were landfilled (US EPA, 2020).
The largest waste landfilled was organic waste which mainly consists of food, accounting for approximately 24% of the total waste. Since landfill space is limited, organic waste piled up in landfills could harm the environment and the health of those living nearby. This is because organic waste in landfills undergoes anaerobic decomposition, creating methane, a greenhouse gas that will affect the temperature and climate of the earth.
Furthermore, methane may endanger the health of individuals, especially those who reside near landfills because a large quantity of methane will replace oxygen in the air and cause breathing problems. Thus, it is important to minimize the amount of organic waste in landfills to prevent the harmful effects of untreated waste.
Households play an important role in mitigating the negative effects of organic waste that piles up in landfills. One way to decrease it is by lowering the number of organic wastes generated and processing the organic waste produced at household levels. As one of the biggest contributors to waste production, households can minimize the quantity of food waste by making an eco-enzyme.
What is an eco-enzyme?
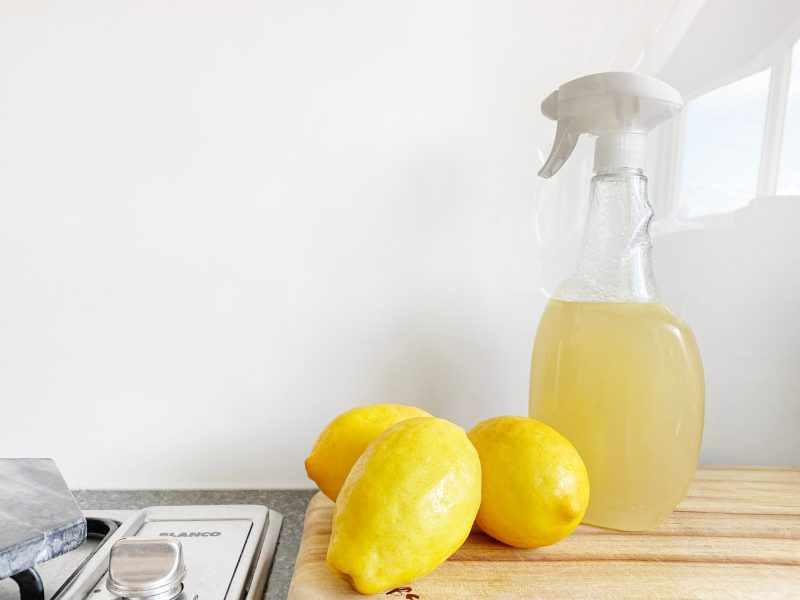
Eco-enzyme is a liquid derived from the fermentation of non-fat organic matter that is used as an environmentally friendly antiseptic because it is made from organic waste and has no detrimental effects on the environment. Vegetable and fruit wastes are organic materials that are commonly utilized in the production of eco-enzymes. Anaerobic respiration, often known as fermentation, is the process by which bacteria derive energy from carbohydrates in an anaerobic (without oxygen) environment, with alcohol or acetic acid as a byproduct (depending upon the type of microorganism) (Whidharma, 2021).
The benefits of eco-enzyme
Eco-enzyme has antimicrobial property due to the production of alcohol or acetic acid from the fermentation process of bacteria that is found in fruit and vegetable waste. Because of their capacity to destroy bacteria and fungi, eco-enzyme may replace most cleaning chemicals for a variety of home cleaning products. Aside from reducing the use of chemical-based cleaning solutions, eco-enzyme has its economic advantage because it decreases the cost of purchasing commercial cleaning supplies. Furthermore, the fruit and vegetable leftovers from processing an eco-enzyme can be used as plant fertilizers.
Ingredients of DIY eco-Enzymes
The process of making eco-enzyme is relatively easy and it only needs a couple of items. These are the ingredients and items that need to be prepared:
- Fruits and vegetable waste. Do not use other types of waste such as meat for eco-enzymes. The decomposition and fermentation processes of meat differ from plants. At unregulated temperatures, meat may degrade fast and may release pathogens.
- Molasses or brown sugar
- Water
- Airtight plastic container. Avoid using glass or metal containers that do not enable gas expansion during the fermentation process.
How to prepare eco-enzymes at home
Eco-enzymes have a ratio of 1:10:3; 1 part of sugar, 10 parts of water, and 3 parts of vegetable or fruit waste. Here are the steps that you can do to create eco-enzymes at home:
- Dilute 100 grams of sugar to 1000ml of water.
- Add 300 grams of fruit or vegetable peels.
- Open the container once a day to release the pressure that has built up within it to avoid bursting during the first month.
- Store in a dry, cool, and well-ventilated location. Allow it to ferment for at least three months before use.
- After 3 months, strain the eco-enzymes, and the liquid is ready to use.
- The remaining waste residue can be utilized for the next batch of enzyme fermentation or can be used as a natural fertilizer.
Additional tips and information about eco-enzymes production:
- Do not fill the container. Allow sufficient space in the bottle for fermentation and ensure that the container is airtight.
- Use lemon peel, orange peel, mango peel, or pandan leaves to develop fresh-smelling eco-enzymes.
- A white layer of biofilm at the top during the fermentation shows the fermentation is going well.
Ways to use eco-enzymes
Here are some ideas and guidance to utilize eco-enzymes at home:
- Eco-enzymes can be used as a detergent alternative by mixing 20-50cc of the liquid into the laundry.
- Eco-enzyme could be a perfect spray cleaner by mixing water with a ratio of 1:25 for removing oil stains.
- Black mold could be removed by soaking and wiping the infected area with 1:25 eco-enzymes to water.
- A deodorizer spray for a cabinet or refrigerator could be made from 1:200 eco-enzymes to water.
- Eco-enzymes could also be used as a plant fertilizer by mixing 1:1000 of eco-enzymes with water.
In conclusion
As one of the biggest contributors to waste, households need to reduce the production of waste to mitigate the detrimental effect of piled-up waste at landfills. Individuals within the household can contribute to minimizing the production of organic waste by producing eco-enzymes. A small step makes a big impact.
The Household Management Science Labs abound with science-based tips and tricks on waste management. Functioning under the network of Life Management Science Labs (LMSL) the lab produces courses, certifications, podcasts, videos, and other learning materials based on the research of the Institute for Life Management Science. Find out more and visit Household Management Science Labs today.
Photo by Precious Plastic Melbourne on Unsplash